Table of contentsAppendices |
6.9 Dynamic Effects: Link and Multi Formatting ObjectsDynamic Effects: Link and Multi Formatting ObjectsIntroduction[top]IntroductionDynamic effects, whereby user actions (including User Agent state) can influence the behavior and/or representation of portions of a document, can be achieved through the use of the formatting objects included in this section:
The switching between subtrees is achieved by using the following three formatting objects: fo:multi-switch, fo:multi-case, and fo:multi-toggle. The result tree structure is shown below. 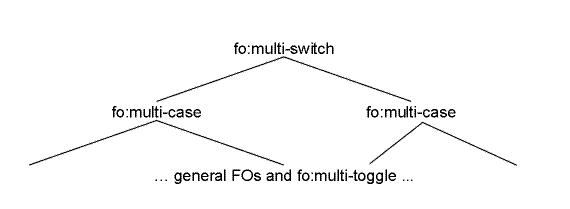
Tree Representation of the Multi Formatting Objects The role of the fo:multi-switch is to wrap fo:multi-case formatting objects, each containing a subtree. Each subtree is given a name on the fo:multi-case formatting object. Activating, for example implemented as clicking on, an fo:multi-toggle causes a named subtree, the previous, the next, or "any" subtree to be displayed; controlled by the "switch-to" property. For "any", an implementation would typically present a list of choices each labeled using the "case-title" property of the fo:multi-case. The initial subtree displayed is controlled by the "starting-state" property on the fo:multi-case. Switching between different property values is achieved by using the fo:multi-properties and fo:multi-property-set formatting objects, and the merge-property-values() function. For example, an fo:multi-property-set can be used to specify various properties for each of the possible values of the active-state property, and merge-property-values() can be used to apply them on a given formatting object. Examples[top]ExamplesExpandable/Collapsible Table of Contents[top]Expandable/Collapsible Table of ContentsInput sample:
<doc>
<chapter><title>Chapter</title>
<p>Text</p>
<section><title>Section</title>
<p>Text</p>
</section>
<section><title>Section</title>
<p>Text</p>
</section>
</chapter>
<chapter><title>Chapter</title>
<p>Text</p>
<section><title>Section</title>
<p>Text</p>
</section>
<section><title>Section</title>
<p>Text</p>
</section>
</chapter>
</doc>
In this example the chapter and section titles are extracted into a table of contents placed at the front of the result. The chapter titles are preceded by an icon indicating either collapsed or expanded state. The section titles are only shown in the expanded state. Furthermore, there are links from the titles in the table of contents to the corresponding titles in the body of the document. The two states are achieved by, for each chapter title, using an fo:multi-switch with a fo:multi-case for each state. The icon is contained in an fo:multi-toggle with the appropriate fo:multi-case "switch-to" property to select the other state. The links in the table of contents are achieved by adding a unique id on the title text in the body of the document and wrapping the title text in the table of contents in an fo:basic-link referring to that id. XSL Stylesheet:
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:fo="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Format"
version='1.0'>
<xsl:template match="doc">
<!-- create the table of contents -->
<xsl:apply-templates select="chapter/title" mode="toc"/>
<!-- do the document -->
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="chapter/title" mode="toc">
<fo:multi-switch>
<fo:multi-case case-name="collapsed" case-title="collapsed"
starting-state="show">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="expanded">
<fo:external-graphic href="plus-icon.gif"/>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="{generate-id(.)}">
<xsl:number level="multiple" count="chapter" format="1. "/>
<xsl:apply-templates mode="toc"/>
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</fo:multi-case>
<fo:multi-case case-name="expanded" case-title="expanded"
starting-state="hide">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="collapsed">
<fo:external-graphic href="minus-icon.gif"/>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="{generate-id(.)}">
<xsl:number level="multiple" count="chapter" format="1. "/>
<xsl:apply-templates mode="toc"/>
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
<xsl:apply-templates select="../section/title" mode="toc"/>
</fo:multi-case>
</fo:multi-switch>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="section/title" mode="toc">
<fo:block start-indent="10mm">
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="{generate-id(.)}">
<xsl:number level="multiple" count="chapter|section" format="1.1 "/>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="chapter/title">
<fo:block id="{generate-id(.)}">
<xsl:number level="multiple" count="chapter" format="1. "/>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:block>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="section/title">
<fo:block id="{generate-id(.)}">
<xsl:number level="multiple" count="chapter|section" format="1.1 "/>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:block>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="p">
<fo:block>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:block>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Result Instance: elements and attributes in the fo: namespace
<fo:multi-switch>
<fo:multi-case case-name="collapsed" case-title="collapsed" starting-state="show">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="expanded">
<fo:external-graphic href="plus-icon.gif">
</fo:external-graphic>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N4">1. Chapter
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</fo:multi-case>
<fo:multi-case case-name="expanded" case-title="expanded" starting-state="hide">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="collapsed">
<fo:external-graphic href="minus-icon.gif">
</fo:external-graphic>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N4">1. Chapter
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
<fo:block start-indent="10mm">
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N11">1.1 Section
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
<fo:block start-indent="10mm">
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N19">1.2 Section
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</fo:multi-case>
</fo:multi-switch>
<fo:multi-switch>
<fo:multi-case case-name="collapsed" case-title="collapsed" starting-state="show">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="expanded">
<fo:external-graphic href="plus-icon.gif">
</fo:external-graphic>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N28">2. Chapter
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</fo:multi-case>
<fo:multi-case case-name="expanded" case-title="expanded" starting-state="hide">
<fo:block>
<fo:multi-toggle switch-to="collapsed">
<fo:external-graphic href="minus-icon.gif">
</fo:external-graphic>
</fo:multi-toggle>
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N28">2. Chapter
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
<fo:block start-indent="10mm">
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N35">2.1 Section
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
<fo:block start-indent="10mm">
<fo:basic-link internal-destination="N43">2.2 Section
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:block>
</fo:multi-case>
</fo:multi-switch>
<fo:block id="N4">1. Chapter
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
<fo:block id="N11">1.1 Section
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
<fo:block id="N19">1.2 Section
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
<fo:block id="N28">2. Chapter
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
<fo:block id="N35">2.1 Section
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
<fo:block id="N43">2.2 Section
</fo:block>
<fo:block>Text
</fo:block>
Styling an XLink Based on the Active State[top]Styling an XLink Based on the Active StateInput sample:
<p>Follow this <xlink:mylink xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
xlink:href="http://www.w3.org/TR"
xlink:title="An Example"
xlink:show="new"
xlink:actuate="onRequest">link</xlink:mylink> to access all
TRs of the W3C.</p>
In this example an fo:basic-link contains a series of fo:multi-property-sets that specify various colors or text-decorations depending on the active state, and a wrapper around the fo:basic-link that allows for the merging of the properties of the fo:multi-properties with those of the appropriate fo:multi-property-sets. XSL Stylesheet:
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:fo="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Format"
version='1.0'>
<xsl:template match="p">
<fo:block>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:block>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="xlink:mylink" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<xsl:variable name="show"><xsl:value-of select="@xlink:show"/>
</xsl:variable>
<fo:multi-properties text-decoration="underline">
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="link" color="blue"/>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="visited" color="red"/>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="active" color="green"/>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="hover" text-decoration="blink"/>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="focus" color="yellow"/>
<fo:wrapper color="merge-property-values()"
text-decoration="merge-property-values()">
<fo:basic-link external-destination="http://www.w3.org/TR"
show-destination="{$show}">
<xsl:attribute name="role">
<xsl:value-of select="@xlink:title"/>
</xsl:attribute>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:wrapper>
</fo:multi-properties>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Result Instance: elements and attributes in the fo: namespace
<fo:block">Follow this
<fo:multi-properties text-decoration="underline">
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="link" color="blue">
</fo:multi-property-set>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="visited" color="red">
</fo:multi-property-set>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="active" color="green">
</fo:multi-property-set>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="hover" text-decoration="blink">
</fo:multi-property-set>
<fo:multi-property-set active-state="focus" color="yellow">
</fo:multi-property-set>
<fo:wrapper color="merge-property-values()"
text-decoration="merge-property-values()">
<fo:basic-link external-destination="http://www.w3.org/TR"
show-destination="new" role="An Example">link
</fo:basic-link>
</fo:wrapper>
</fo:multi-properties> to access all
TRs of the W3C.
</fo:block>
fo:basic-link[top]fo:basic-linkCommon Usage: The fo:basic-link is used for representing the start resource of a simple one-directional single-target link. The object allows for traversal to the destination resource, typically by clicking on any of the containing areas. Areas: The fo:basic-link formatting object generates one or more normal inline-areas. The fo:basic-link returns these areas, any page-level-out-of-line areas, and any reference-level-out-of-line areas returned by the children of the fo:basic-link. NOTE: Constraints: No area may have more than one normal child area returned by the same fo:basic-link formatting object. The children of each normal area returned by an fo:basic-link must satisfy the constraints specified in [area-inlinebuild] . Contents: (#PCDATA|%inline;|%block;)* In addition this formatting object may have a sequence of zero or more fo:markers as its initial children. The following properties apply to this formatting object:
fo:multi-switch[top]fo:multi-switchCommon Usage: The fo:multi-switch wraps the specification of alternative sub-trees of formatting objects (each sub-tree being within an fo:multi-case), and controls the switching (activated via fo:multi-toggle) from one alternative to another. The direct children of an fo:multi-switch object are fo:multi-case objects. Only a single fo:multi-case may be visible at a single time. The user may switch between the available multi-cases. Each fo:multi-case may contain one or more fo:multi-toggle objects, which controls the fo:multi-case switching of the fo:multi-switch. NOTE: Areas: The fo:multi-switch formatting object does not generate any areas. The fo:multi-switch formatting object returns the sequence of areas returned by the currently visible fo:multi-case. If there is no currently visible fo:multi-case no areas are returned. Trait Derivation: The currently-visible-multi-case trait has as its initial value a reference to the first fo:multi-case child that has a value of "show" of the starting-state trait. If there is no such child, it has a value indicating that there is no currently visible fo:multi-case. When an fo:multi-toggle is actuated, its closest ancestral fo:multi-switch's currently-visible-multi-case trait value changes to refer to the fo:multi-case selected by the "switch-to" property value of the fo:multi-toggle. Once the currently-visible-multi-case trait gets a value indicating that there is no currently visible fo:multi-case, it becomes impossible to actuate an fo:multi-toggle in this fo:multi-switch. Constraints: The order of the sequence of areas returned by the fo:multi-switch is the same as the order of the areas returned by the currently visible fo:multi-case. Contents: (multi-case+) The following properties apply to this formatting object: fo:multi-case[top]fo:multi-caseCommon Usage: The fo:multi-case is used to contain (within an fo:multi-switch) each alternative sub-tree of formatting objects among which the parent fo:multi-switch will choose one to show and will hide the rest. Areas: The fo:multi-case formatting object does not generate any areas. The fo:multi-case formatting object returns the sequence of areas created by concatenating the sequences of areas returned by each of the children of the fo:multi-case. Constraints: The order of concatenation of the sequences of areas returned by the children of the fo:multi-case is the same order as the children are ordered under the fo:multi-case. Contents: (#PCDATA|%inline;|%block;)* An fo:multi-case is only permitted to have children that would be permitted to be children of the parent of the fo:multi-switch that is the parent of the fo:multi-case, except that an fo:multi-case may not contain fo:marker children. In particular, it can contain fo:multi-toggle objects (at any depth), which controls the fo:multi-case switching. This restriction applies recursively. NOTE: The following properties apply to this formatting object: fo:multi-toggle[top]fo:multi-toggleCommon Usage: The fo:multi-toggle is typically used to establish an area that when actuated (for example implemented as "clicked"), has the effect of switching from one fo:multi-case to another. The "switch-to" property value of the fo:multi-toggle typically matches the "case-name" property value of the fo:multi-case to switch to. Areas: The fo:multi-toggle formatting object does not generate any areas. The fo:multi-toggle formatting object returns the sequence of areas created by concatenating the sequences of areas returned by each of the children of the fo:multi-toggle. Each of the areas returned by the fo:multi-toggle has a switch-to trait with the same value as on the returning fo:multi-toggle. Constraints: The order of concatenation of the sequences of areas returned by the children of the fo:multi-toggle is the same order as the children are ordered under the fo:multi-toggle. Activating an area returned by an fo:multi-toggle causes a change to the value of the currently-visible-multi-case of the closest ancestor fo:multi-switch. (See [switch-to] for how the switch-to value selects an fo:multi-case.) Contents: (#PCDATA|%inline;|%block;)* An fo:multi-toggle is only permitted as a descendant of an fo:multi-case. The following properties apply to this formatting object: fo:multi-properties[top]fo:multi-propertiesCommon Usage: The fo:multi-properties is used to switch between two or more property sets that are associated with a given portion of content. NOTE: The direct children of an fo:multi-properties formatting object is an ordered set of fo:multi-property-set formatting objects followed by a single fo:wrapper formatting object. The properties, specified on the fo:wrapper, that have been specified with a value of "merge-property-values()" will take a value that is a merger of the value on the fo:multi-properties and the specified values on the fo:multi-property-set formatting objects that apply. Areas: The fo:multi-properties formatting object does not generate any areas. The fo:multi-properties formatting object returns the sequence of areas created by concatenating the sequences of areas returned by each of the children of the fo:multi-properties. Constraints: The order of concatenation of the sequences of areas returned by the children of the fo:multi-properties is the same order as the children are ordered under the fo:multi-properties. Contents: (multi-property-set+,wrapper) The properties that should take a merged value shall be specified with a value of "merge-property-values()". This function, when applied on an fo:wrapper that is a direct child of an fo:multi-properties, merges the applicable property definitions on the fo:multi-property-set siblings. The following properties apply to this formatting object: fo:multi-property-set[top]fo:multi-property-setCommon Usage: The fo:multi-property-set auxiliary formatting object is used to specify an alternative set of formatting properties that can be used to provide an alternate presentation of the children flow objects of the fo:wrapper child of the parent of this fo:multi-property-set. Areas: The fo:multi-property-set formatting object does not generate or return any areas. It simply holds a set of traits that may be accessed by expressions. Constraints: None. Contents: EMPTY The following properties apply to this formatting object: |
